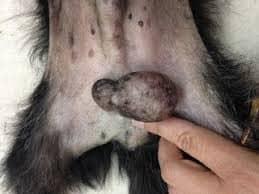
As a cherished member of the family, our dogs deserve the best care possible, and part of that care includes being attentive to their health and well-being. While many pet owners are familiar with common ailments such as ear infections or skin issues, conditions affecting the scrotum in male dogs often go overlooked. Understanding the signs, causes, and treatments of scrotal diseases is essential for ensuring your furry friend remains happy and healthy.
In this article, we will explore the various ailments that can affect the scrotum, helping you recognize any unusual symptoms and providing guidance on how to seek appropriate treatment. Join us as we delve into this important topic, ensuring you’re well-equipped to care for your canine companion’s needs.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Common Scrotal Conditions in Dogs
- Recognizing the Signs: What to Look For
- Identifying the Causes Behind Scrotal Diseases
- Treatment Options: Keeping Your Dog Healthy and Comfortable
- Q&A
- Final Thoughts
Understanding Common Scrotal Conditions in Dogs
Scrotal conditions in dogs can vary widely, often presenting with different signs and symptoms that pet owners should be vigilant about. Some common issues include scrotal dermatitis, hydrocele, testicular tumors, and torsion of the spermatic cord. Each condition has its unique set of causes, which may range from skin irritations due to allergies, infections, or trauma to more serious concerns like tumors or torsion. As a responsible pet owner, recognizing early warning signs such as swelling, discoloration, or unusual behaviors like excessive licking of the area is crucial. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of scrotal conditions typically involves a thorough physical examination, potentially accompanied by diagnostic tests like ultrasound or biopsy. After determining the underlying cause, treatment options may include medication, surgical intervention, or supportive care. Here’s a brief overview of some common conditions and their treatments:
| Condition | Signs | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Scrotal Dermatitis | Redness, itching, hair loss | Topical medication, steroids |
| Hydrocele | Swelling of the scrotum | Surgical drainage, observation |
| Testicular Tumors | Swelling, lumps | Orchiectomy (surgery) |
| Torsion | Severe pain, swelling | Emergency surgery |
Prevention strategies can also play a pivotal role in maintaining your pet’s scrotal health. Regular veterinary checkups, prompt attention to any skin issues, and a balanced diet can all help mitigate the risk of developing these conditions. Educating yourself about the common signs and being proactive can ensure your furry friend remains healthy and happy.
Recognizing the Signs: What to Look For
Identifying potential issues with your dog’s scrotum requires careful observation of their behavior and physical state. Common signs that may indicate a problem include:
- Swelling or Lumps: Unusual growths or inflammation can signify underlying conditions.
- Discharge: Any discharge from the scrotum should be treated as a potential red flag.
- Excessive Grooming: If your dog is obsessively licking or biting at the area, this could indicate discomfort or irritation.
- Pain or Discomfort: Watch for signs of pain, such as whimpering when touched or reluctance to engage in normal activities.
Additional symptoms may vary based on the specific ailment but can include changes in urination habits or lethargy. It’s essential to monitor your dog closely for any of the following:
- Foul Odor: A strong or unpleasant smell can be an indication of infection.
- Behavioral Changes: Withdrawn behavior or reduced appetite can hint at underlying discomfort.
- Temperature Changes: A higher than normal body temperature may suggest an infection or inflammation.
Identifying the Causes Behind Scrotal Diseases
Scrotal diseases in dogs can stem from a variety of underlying issues, often linked to anatomical, hormonal, or infectious factors. Common causes include:
- Infections: Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections can lead to inflammation and discomfort within the scrotal area.
- Testicular tumors: Both benign and malignant tumors can develop, affecting the health of the testes and surrounding structures.
- Hernias: Inguinal or scrotal hernias may occur when abdominal contents protrude, leading to potential complications.
- Hormonal imbalances: Conditions like hyperadrenocorticism can influence the scrotum’s condition and function.
Understanding the symptoms and seeking veterinary guidance early can significantly improve outcomes for affected dogs. Identification of the causative factors is essential for effective treatment, which may involve:
| Cause | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Infections | Antibiotics or antifungal medications |
| Testicular tumors | Possible surgical removal and chemotherapy |
| Hernias | Surgical correction |
| Hormonal imbalances | Medication to regulate hormone levels |
Treatment Options: Keeping Your Dog Healthy and Comfortable
Ensuring your dog remains in optimal health involves a proactive approach to their well-being, especially when it comes to conditions affecting sensitive areas like the scrotum. Common treatment options for scrotal diseases include medications, surgical interventions, and home remedies. For infections or inflammation, your veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate discomfort and treat underlying causes. In more severe cases, surgical options might be necessary, such as the removal of tumors or cysts to prevent further complications.
In addition to medical treatments, an emphasis on regular check-ups can help catch issues early. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through balanced nutrition and adequate exercise is crucial for your dog’s overall health. Consider incorporating the following practices into your routine:
- Regular grooming to monitor for abnormalities
- Routine veterinary check-ups at least once a year
- Proper hygiene practices to minimize infections
By being attentive to your dog’s needs and seeking treatment early, you can help ensure their comfort and longevity.
Q&A: Diseases of the Scrotum in Dogs: Signs, Causes, and Treatments
Q1: What are some common diseases of the scrotum in dogs?
A1: Common diseases affecting the scrotum in dogs include scrotal dermatitis, scrotal hematomas, testicular tumors, and infections such as orchitis or epididymitis. Each condition can have varying signs and may require different treatment approaches.
Q2: What are the signs that my dog may have a scrotal issue?
A2: Signs of scrotal problems can include swelling, redness, or irritation of the scrotum, excessive licking or scratching in the area, pain or discomfort (which may show as whining or avoidance of touch), as well as unusual discharge or changes in the size or shape of the testicles. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult your veterinarian.
Q3: What causes scrotal diseases in dogs?
A3: Scrotal diseases can arise from various causes, including allergies that lead to dermatitis, trauma or injury leading to hematomas, hormonal imbalances that contribute to tumors, or bacterial infections that affect the testes or surrounding structures. Factors such as age, breed, and overall health can also influence the likelihood of developing these conditions.
Q4: How are scrotal diseases diagnosed in dogs?
A4: Diagnosis typically begins with a thorough physical examination by your veterinarian, who may assess the scrotum and perform blood tests or imaging studies, such as ultrasound, to evaluate the internal structures. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to determine the nature of a mass or lesion.
Q5: What are the treatment options for scrotal diseases in dogs?
A5: Treatment depends on the specific condition diagnosed. For dermatitis, topical medications and antihistamines may be prescribed. In cases of scrotal hematomas or tumors, surgery might be necessary. Infections are usually treated with antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications. Always consult your veterinarian for the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to your dog’s needs.
Q6: Can scrotal diseases be prevented?
A6: While not all scrotal diseases are preventable, good hygiene, regular veterinary checkups, and prompt attention to any signs of discomfort can help maintain your dog’s health. Additionally, discussing options like neutering with your veterinarian can prevent certain conditions associated with unneutered dogs.
Q7: When should I take my dog to the vet regarding scrotal health?
A7: It’s best to take your dog to the vet if you notice any changes in their scrotal area, especially if these changes are accompanied by signs of pain, discomfort, or unusual behavior. Early intervention can often lead to better outcomes and more effective treatment.
Q8: How can I support my dog during recovery from a scrotal condition?
A8: Support your dog by following your veterinarian’s post-treatment care instructions, which may include administering medications, managing activity levels, and keeping the area clean. Providing comfort, maintaining a calm environment, and monitoring for any signs of complications will also help your dog recover more smoothly.
Feel free to consult your veterinarian for any specific concerns regarding your dog’s scrotal health, as they can provide personalized guidance based on your pet’s unique situation.
Final Thoughts
understanding the diseases of the scrotum in dogs is essential for every pet owner. By recognizing the signs and symptoms early on, you can ensure your furry companion receives timely veterinary care, which is crucial for effective treatment and a speedy recovery. Whether it’s a straightforward issue like dermatitis or something more complex like tumors, being informed empowers you to take the best possible care of your dog. Remember, regular check-ups and open communication with your veterinarian can make a significant difference in your pet’s health. Don’t hesitate to reach out with any concerns—after all, a happy and healthy dog means a happy owner! Thank you for taking the time to learn about this important topic, and we wish you and your beloved pets all the best in your journey together.